- MODULE 1: Introduction to ABI
- Module Introduction
- Take the Pre-test
- a) A person’s abilities & life span
- b) What is ABI?
- c) Causes of ABI
- d) Incidence
- e) The brain
- f) Severity of ABI
- g) Cause to impact
- h) Rehabilitation
- i) Rehabilitation stages & pathways
- j) Common effects
- k) Impacts on life
- l) People with ABI
- m) Family and friends
- n) Key messages and
Tools to explore in Module 2 - o) Building skills
- Take the Post-test
h) Rehabilitation
i) The essence
SLIDES:
To pause: Hover mouse over slide. To continue: move mouse off slide.
To go to a specific slide: Click on slide numbers below.
ii) Rehabilitation aims to facilitate ongoing recovery.
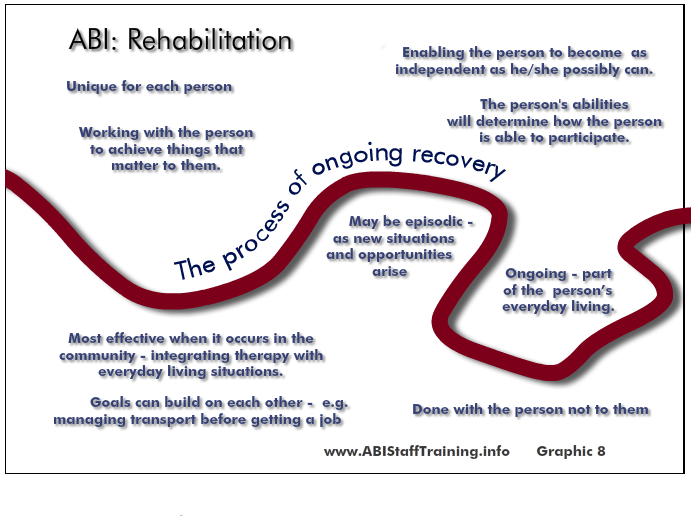
Rehabilitation enables a person to become as independent as they possibly can. The goal is for the person to return to their previous abilities, activities and way of life as much as they possibly can. It means enabling the person to live with their remaining abilities and develop strategies to enable them to compensate and overcome new difficulties.
The process of rehabilitation experienced by each person is unique. Just as a brain injury is unique, the type of rehabilitation program the person is engaged in is uniquely tailored to target individual needs. Rehabilitation addresses specific areas of physical difficulty, thinking or cognitive processing, perception, social skills and relationships. It also addresses broader areas of returning to work, getting about in the community, and adjusting to changes a person may experience following a brain injury.
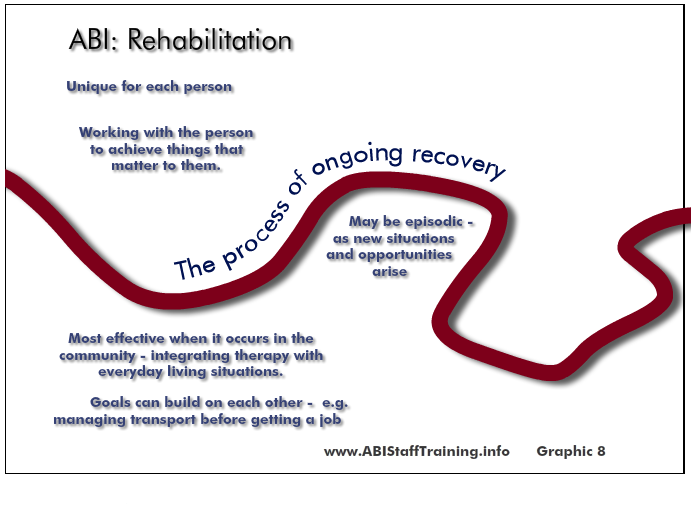
Rehabilitation goals can build on each other, for example managing transport before getting a job.
Rehabilitation is ongoing.
It may also be episodic - as new situations and opportunities arise.
Rehabilitation is not something that is done to the person, rather with the person.
Rehabilitation is based on working with the person to achieve things that matter to them. Therefore, for it to be successful, the individual needs to participate actively in the rehabilitation process. The type of rehabilitation offered needs to be meaningful and relevant to the person. This means the person, their culture, pre-injury lifestyle, family and environment are critical to ensuring the success of rehabilitation.
The person's abilities will determine how the person is able to participate in the rehabilitation process.
Where recovery to the person's pre-injury life pathway is not possible rehabilitation involves choosing another meaningful but different pathway to a life worth living.
(c) Copyright - See: Toolkit B. Working Together Promoting Independence - www.TBIStaffTraining.info
Answer the following questions
Rehabilitation enables a person to become as independent as they possibly can.
Rehabilitation with people with ABI is usually time limited.
There are pre-defined rehabilitation pathways for people with ABI
Rehabilitation for people with ABI can be episodic as new situations and opportunities arise
Which of the following are true?